quantitative population sample|probability sampling examples : distribute First, you need to understand the difference between a population and a sample, and identify the target population of your research. 1. The populationis the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about. 2. The sampleis the specific group of individuals that you will collect data from. The population can be . See more WEB4 dias atrás · Ace Combat: Assault Horizon features online multiplayer capabilities, similar to its 2007 predecessor. The game's feature mode, Capital Conquest, has players from both NRF and NATO either attacking or defending cities such as Paris or Washington.
{plog:ftitle_list}
web(Rank X) Legion Escadora (Rank S) Legion Escadora to (Rank X) Legion Escadora(Rank X) Eternal Cosmic (Rank S) Eternal Cosmic to (Rank X) Eternal Cosmic(Rank X) Code T .
First, you need to understand the difference between a population and a sample, and identify the target population of your research. 1. The populationis the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about. 2. The sampleis the specific group of individuals that you will collect data from. The population can be . See moreProbability sampling means that every member of the population has a chance of being selected. It is mainly used in quantitative research. If you want to produce results that . See moreIn a non-probability sample, individuals are selected based on non-random criteria, and not every individual has a chance of being included. This type of sample is easier and cheaper to access, but it has a higher risk of sampling bias. That means the inferences you . See moreIf you want to know more about statistics, methodology, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples. See more
Hypothesis testing is a fundamental aspect of quantitative research, employed to make inferences or draw conclusions about populations based on sample data. This test . A representative sample mirrors the properties of the population. Using this approach, researchers can generalize the results from their sample to the population. Performing valid inferential statistics requires a strong .Sampling in quantitative research is a critical component that involves selecting a representative subset of individuals or cases from a larger population and often employs sampling techniques . A population is the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about. A sample is the specific group that you will collect data from. The size of the sample is always less than the total size of the population. In .
In quantitative research, collecting data from an entire population of a study is impractical in many instances. It squanders resources like time and money which can be . Probability sampling is a sampling method that involves randomly selecting a sample, or a part of the population that you want to research. It is also sometimes called .Researchers focus on the specific techniques that will yield highly representative samples (i.e., samples that are very much like the population). Quantitative researchers tend to use a type of .
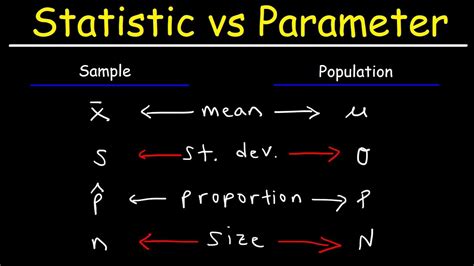
These sample statistics are properties of my data set, and although they are fairly similar to the true population values, they are not the same. In general, sample statistics are the things you can calculate from your . The sample size of a quantitative study is the number of people who complete questionnaires in a research project. It is a representative sample of the target audience in which you are interested. . Some represent smaller . Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analyzing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, . You can test your hypothesis or use your sample data to estimate the population parameter.
Athletes of various activities from Punjab University (n-300) were taken as a population of the study and thus 100 athletes were selected as sample by using the available sample technique. • Cluster sampling: Population is divided into mutually exclusive groups (e.g. classes) and random sample of groups are drawn from the population. • Multistage sampling : Combining various sampling methods, for example, beginning with simple random sampling of locations, followed by systematic sampling of participants in each location. Quantitative Research. Quantitative research is a type of research that collects and analyzes numerical data to test hypotheses and answer research questions.This research typically involves a large sample size and uses statistical analysis to make inferences about a population based on the data collected.As you might have guessed, drawing a simple random sample can be quite tedious. Systematic sampling A researcher divides a study population into relevant subgroups then draws a sample from each subgroup. techniques are somewhat less tedious but offer the benefits of a random sample. As with simple random samples, you must be able to produce a .
statistical parameters vs population
sample population in the same manner such resulting discrepancies are termed as sampling errors. The sampling errors cannot be completely eliminated but may be minimized by choosing Example 1: Research Study: Investigating the prevalence of stress among high school students in a specific city and its impact on academic performance. Population: All high school students in a particular city Sampling Frame: The sampling frame would involve obtaining a comprehensive list of all high schools in the specific city. A random selection of schools .We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. A sample of 200 people living nearby is collected. Purposive: Sample for the study is selected based on the perception or knowledge or judgement of the researcher about the required sample set. Thus, sample units are handpicked from the population. Suitable for a large population who are difficult to reach.
This can be done by increasing the sample size. Population size. Population size is the total amount of people in the group you're trying to study. If you were taking a random sample of people across the U.K., then your population size would be just over 68 million (as of 09 August 2021). Standard deviation
The study population, or "sampling frame," refers to the collection of individuals or units from which a sample is drawn, highlighting the importance of selecting a representative sample to ensure .
The value of quantitative research is that results gained from numerical data in a sample population can be used to generalize or explain a particular phenomenon in the general population (Babbie 2016). Quantitative research can be either experimental or descriptive (nonexperimental, i.e., describes a population in specific terms). Sampling methods in psychology refer to strategies used to select a subset of individuals (a sample) from a larger population, to study and draw inferences about the entire population. Common methods include random sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and convenience sampling. Proper sampling ensures representative, generalizable, and valid .
A good maximum sample size is usually 10% as long as it does not exceed 1000. A good maximum sample size is usually around 10% of the population, as long as this does not exceed 1000. For example, in a population of 5000, 10% . sample population by the w ay of generating numerical d ata. The purpose of this study is to provide some important fundamental concepts of quantitative research to the common readers for the .

The quantitative researcher seeks a sample that is representative of the population of interest so that they may properly generalize the results (e.g., if 80 percent of first-gen students in the sample were concerned with costs of .
Generalizability: Quantitative research aims to generalize findings from a sample to a larger population. It seeks to draw conclusions that apply to a broader group beyond the specific sample being studied. Quantitative Research Examples. Below are 3 examples of quantitative research:
In statistics as well as in quantitative methodology, the set of data are collected and selected from a statistical population with the help of some defined procedures. There are two different types of data sets namely, population and sample.Chapter 3 Sample - Quantitative. Our whole universe was in a hot, dense state Then nearly fourteen bill. View more. Course. STRUCTURE (AE3710) 77 Documents. . Population and Sample of the Study. The respondents of the study are college students of Bulacan State University (Main Campus). BulSU was the only state university in Bulacan with . The entire purpose of “probability-based random sampling is generalization from the sample to a population.”(Patton, 2002: 273). Finally, these determinations are made a priori. For quantitative projects the adequacy of the sample size must be determined before the
Medical and population health science researchers frequently make ambiguous statements about whether they believe their study sample or results are representative of some (implicit or explicit) target population. This article provides a comprehensive definition of representativeness, with the goal of capturing the different ways in which a study can be representative of a target . The following are some of the characteristics of descriptive research: Quantitativeness. Descriptive research can be quantitative as it gathers quantifiable data to statistically analyze a population sample. These numbers can show patterns, connections, and trends over time and can be discovered using surveys, polls, and experiments.
In other words, it refers to how much a statistic varies from sample to sample within a population. The larger the sample size, the smaller the variability between samples will be. So, the large sample size makes for a better, more reliable statistic. Size of a Sample. The size of a sample (often called the number of observations) is important.Whenever we hear the term ‘population,’ the first thing that strikes our mind is a large group of people. In the same way, in statistics population denotes a large group consisting of elements having at least one common feature. The term is often contrasted with the sample, which is nothing but a part of the population that is so selected to represent the entire group. Quantitative methods emphasize objective measurements and the statistical, mathematical, or numerical analysis of data collected through polls, . An experimental design includes subjects measured before and after a particular treatment, the sample population may be very small and purposefully chosen, and it is intended to establish causality .Other common quantities, specifically for quantitative variables, include the proportion of observations that are equal to one specific value. . We can also calculate the proportion of local hosts for our sample and for our population. Here, we will need to make a decision on what to do with missing data. Similar to the process followed in .

how hard is the mn knowledge test

quantitative research guidelines
2 dias atrás · -, 视频播放量 1191、弹幕量 0、点赞数 123、投硬币枚数 13、收藏人数 19、转发人数 1, 视频作者 失足后去弹贝斯, 作者简介 教学 购琴请私信 ️,相关视频:《想做你的奴隶和主人》i wanna be your slave - basscover,《贝斯手活不好主要怪没有六 .
quantitative population sample|probability sampling examples